- 13 May 2025
Symptoms of a Failing Car Battery and Engine Issues

When your vehicle unexpectedly refuses to start on a cold morning or leaves you stranded in a parking lot, a failing car battery is often the culprit. Understanding the symptoms of a failing car battery can save you from inconvenient breakdowns and potentially costly repairs. Car batteries typically last between three to five years, depending on usage conditions and maintenance, but various factors can accelerate their deterioration. This comprehensive guide explores the telltale signs of battery failure, how these issues affect your engine performance, and practical solutions to extend your battery’s lifespan.
Early Warning Signs of Battery Deterioration
Sluggish Engine Cranking
One of the earliest and most noticeable symptoms of a failing car battery is a sluggish engine start. When you turn the key or push the ignition button, you might hear the engine cranking slowly or laboring before eventually starting. This occurs because the deteriorating battery cannot deliver the necessary current to the starter motor. The starter requires significant power to turn the engine over, and a weakened battery simply cannot provide the required energy burst.
Dimming Headlights and Electrical Issues
Your vehicle’s electrical system depends entirely on a healthy battery. As a car battery begins to fail, you may notice dimming headlights, particularly when idling or during nighttime driving. Other electrical components may also exhibit unusual behavior—power windows might operate more slowly than usual, the radio might cut out intermittently, or dashboard lights might flicker. These symptoms occur because the failing battery cannot consistently maintain voltage across all electrical systems.
Dashboard Warning Lights
Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems that can detect battery issues before they become critical. If your battery is failing, you might see a battery warning light (typically shaped like a battery) illuminate on your dashboard. Some vehicles display a “CHECK BATTERY” or “BATTERY LOW” message. Don’t ignore these warnings—they’re designed to alert you to potential problems before you experience a complete battery failure.
Swollen Battery Case
Physical inspection can reveal important clues about battery health. A failing car battery might develop a swollen or bloated case due to excessive heat exposure or internal short circuits. This swelling happens when the battery’s electrolyte solution overheats and produces excessive hydrogen gas. A swollen battery is dangerous and requires immediate replacement, as it could potentially leak corrosive acid or even explode under certain conditions.
Unusual Odors
If you detect a distinctive rotten egg smell (hydrogen sulfide) when opening your hood, this could indicate a failing car battery that’s leaking gas. This occurs when the battery overcharges, causing the electrolyte solution to heat up and release sulfuric fumes. This symptom should never be ignored, as these emissions are both unpleasant and potentially hazardous.
Advanced Symptoms of Battery Failure
Complete Electrical System Failure
As battery deterioration progresses, you may experience more dramatic electrical failures. These can include:
- Complete power loss while driving
- Inability to start the vehicle at all
- Erratic behavior from electronic systems
- Total dashboard blackout
When a car battery reaches this stage of failure, the vehicle’s alternator—which normally recharges the battery while driving—can’t compensate for the severely degraded battery capacity.
Frequent Jump-Starts Required
If you find yourself needing jump-starts with increasing frequency, this is a clear indicator of advanced battery deterioration. While occasional jump-starts might be necessary due to leaving lights on or extended periods of non-use, a healthy battery should hold its charge reliably once recharged. Needing repeated jump-starts suggests the battery has lost its ability to maintain a charge and requires replacement.
Corroded Battery Terminals
Battery terminals naturally accumulate some corrosion over time, but excessive buildup of whitish, blue, or greenish powder around the terminals suggests a failing car battery that’s leaking acid or emitting gases. This corrosion creates resistance in the electrical connections, exacerbating starting problems and potentially damaging your vehicle’s electrical system. While terminal cleaning can temporarily improve connections, significant corrosion often accompanies a battery nearing the end of its useful life.
How Battery Problems Affect Engine Performance
Engine Starting Issues
The most direct impact of battery problems on engine performance is difficulty starting. The engine’s starter motor requires substantial electrical current to overcome the compression resistance of the engine cylinders. When battery power is insufficient, engine starting becomes unreliable or impossible. In fuel-injected vehicles, the battery also powers the fuel pump and injection system, meaning even if the engine does crank, it might not receive the fuel needed to run properly.
Engine Stalling and Misfires
A healthy charging system, including the battery, alternator, and voltage regulator, maintains stable electrical power for engine management systems. When battery performance degrades, voltage fluctuations can occur, potentially causing engine stalling or misfires. Modern engines rely heavily on precise electronic control of fuel injection and ignition timing—functions that require stable voltage to operate correctly. Engine issues that appear to resolve themselves after a battery replacement often stem from these voltage-related problems.
Fuel System Operation
Many drivers don’t realize that engine issues like hesitation, rough idling, or poor acceleration can sometimes be traced to a failing car battery. In contemporary vehicles, the fuel pump, fuel injectors, and related sensors all depend on consistent electrical power. When battery voltage drops below normal levels, these components may not function optimally, resulting in combustion inefficiencies and noticeable drivability problems.
Impact on Engine Control Module
The Engine Control Module (ECM)—sometimes called the Engine Control Unit (ECU)—is the computerized brain of your vehicle. This sophisticated component constantly adjusts engine parameters based on input from numerous sensors. A failing battery can cause voltage drops that reset the ECM or cause it to operate in “limp mode,” a fail-safe program that restricts engine performance to prevent damage. These voltage irregularities can even damage sensitive electronic components over time, potentially leading to expensive repairs.
The Connection Between Battery Health and Long-Term Engine Health
Alternator Strain
When a car battery begins failing, the alternator must work harder to maintain system voltage, which can lead to premature alternator failure. The alternator is designed to maintain battery charge during normal operation, not to fully charge a significantly depleted battery. Consistently operating with a failing battery forces the alternator to run at maximum output, generating excess heat and accelerating wear on its internal components.
Starter Motor Damage
Similarly, a failing car battery forces the starter motor to operate with insufficient power. This causes increased heat generation within the starter and can lead to premature failure of this critical component. Replacing a starter motor is significantly more expensive and labor-intensive than replacing a battery, making preventative battery maintenance a wise economic decision.
Electronic System Strain
Modern vehicles contain dozens of electronic control units managing everything from engine timing to climate control. These sensitive components are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges. A failing battery creates voltage fluctuations that can gradually damage these electronic systems, potentially leading to erratic behavior, fault codes, and expensive diagnostic challenges.
Factors Accelerating Battery Deterioration
Temperature Extremes
Both extremely hot and cold conditions accelerate battery deterioration. In hot climates, battery fluid evaporates more quickly, and internal components degrade faster. In cold weather, the chemical reactions within the battery slow down, reducing available power precisely when the engine requires more energy to start. These temperature-related stresses significantly shorten battery lifespan.
Short-Distance Driving Patterns
Vehicles used primarily for short trips often experience premature battery failure. This driving pattern doesn’t allow the alternator sufficient time to recharge the battery after the energy-intensive starting process. Over time, this creates a net deficit in the battery’s charge level, leading to sulfation—a process where lead sulfate crystals build up on the battery plates, reducing capacity and efficiency.
Parasitic Drains
Modern vehicles contain numerous systems that draw small amounts of power even when the vehicle is off, such as security systems, clocks, and computer memory functions. While these draws are normally minimal, electrical faults can create excessive parasitic drains that deplete the battery over time. Aftermarket accessories installed incorrectly can also create abnormal power draws that accelerate battery failure.
Vibration and Physical Damage
Excessive vibration from driving on rough roads or from a loose battery mount can damage a battery’s internal plates and connections. This physical damage reduces battery capacity and lifespan. Always ensure batteries are securely mounted using the manufacturer’s recommended hardware.
Diagnosing Battery Problems Accurately
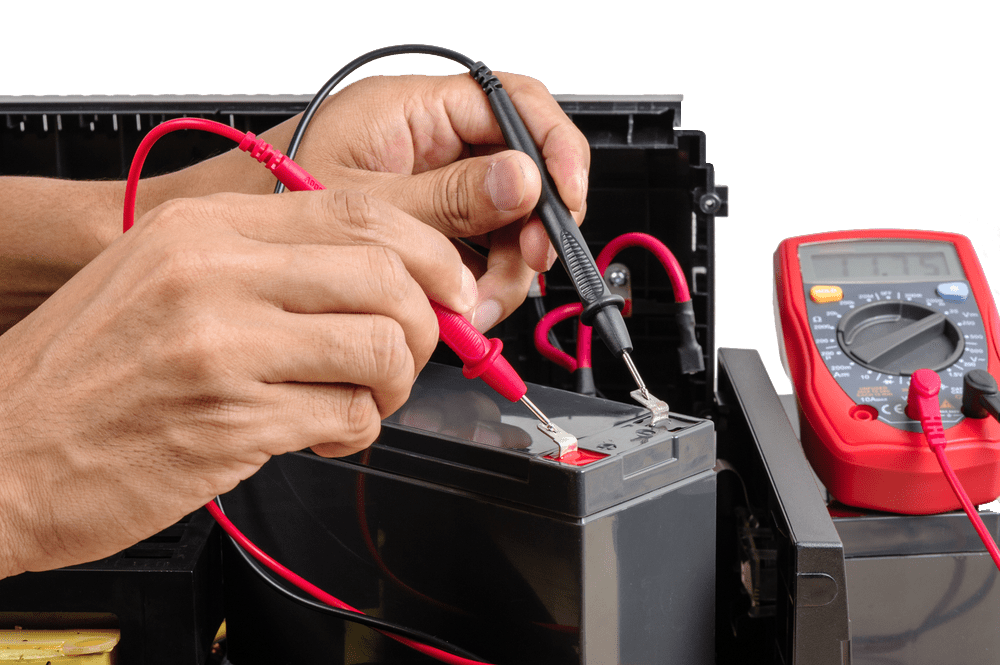
Voltage Testing
A multimeter provides a simple first step in battery diagnosis. A healthy 12-volt battery should read approximately 12.6 volts when the engine is off and 13.7 to 14.7 volts when the engine is running. Readings below 12.4 volts with the engine off suggest a partially discharged battery, while readings below 12 volts indicate significant discharge requiring immediate attention.
Load Testing
Voltage readings alone can be misleading, as a failing battery might show normal voltage when under no load. A proper load test applies a controlled electrical demand to the battery while monitoring voltage. This test reveals the battery’s ability to deliver current under stress—a crucial factor in cold-weather starting. Professional automotive shops and many auto parts stores offer free battery load testing services.
Charging System Analysis
Since battery problems can sometimes be caused by alternator issues, a complete diagnosis should include checking the charging system. A healthy alternator should produce 13.7 to 14.7 volts at idle. Readings outside this range suggest alternator problems that could affect battery life and engine performance. Some alternator issues can mimic the symptoms of a failing car battery, making proper diagnosis essential.
Parasitic Draw Testing
If a battery repeatedly discharges despite appearing healthy in other tests, a parasitic draw test can identify abnormal current drains. This test uses an ammeter to measure the current flow when the vehicle is off. Most modern vehicles should draw less than 50 milliamps. Higher readings suggest an electrical problem that’s draining the battery.
Battery Maintenance and Prevention Strategies
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Simple preventative maintenance can extend battery life significantly:
- Check battery terminals for corrosion monthly
- Clean terminals with a mixture of baking soda and water when necessary
- Ensure terminal connections are tight but not overtightened
- Inspect the battery case for cracks or bulging
- Check that the battery is securely mounted to prevent vibration damage
Managing Seasonal Challenges
Different seasons present unique battery challenges:
- In summer, check fluid levels more frequently in conventional batteries
- Before winter, have your battery professionally load-tested
- Consider a battery tender (trickle charger) for vehicles used infrequently
- Park in garages or shaded areas when possible to minimize temperature extremes
Driving Habits for Battery Health
Certain driving habits can promote battery longevity:
- Take occasional longer drives if your typical usage involves short trips
- Minimize the use of electrical accessories when the engine isn’t running
- Turn off all accessories before shutting down the engine to reduce initial load on restart
- Avoid excessive use of the remote starter, which can cycle the battery without providing charging time
When to Replace Your Battery
Age Considerations
Even with perfect maintenance, batteries have a finite lifespan. Most automotive batteries are designed to last 3-5 years, though premium models may last longer. If your battery is approaching this age range, consider proactive replacement, especially before seasons with temperature extremes.
Performance Deterioration
When you notice multiple symptoms of a failing car battery, replacement is typically more economical than attempting to nurse along a deteriorating unit. Modern batteries are largely maintenance-free and relatively affordable compared to the potential costs of being stranded or damaging other electrical components.
Emergency vs. Planned Replacement
Emergency battery replacements—when you’re already experiencing failure—often lead to:
- Higher costs due to limited shopping options
- Potential for being stranded in unsafe locations
- Possibility of damage to other electrical components
- Stress and inconvenience of unexpected breakdown
Planned replacement based on regular testing and age provides:
- Opportunity to research and select optimal replacement
- Convenient timing and location for service
- Prevention of related electrical system damage
- Peace of mind, especially before travel or seasonal changes
Conclusion
The symptoms of a failing car battery often manifest as more than just starting troubles—they can affect overall engine performance, electrical system reliability, and even long-term component health. By recognizing early warning signs like sluggish starting, dimming lights, and dashboard warning indicators, you can address battery issues before they leave you stranded or cause more extensive engine problems.
Regular maintenance, appropriate driving habits, and proactive testing can significantly extend battery life and prevent many of the engine issues associated with electrical system problems. When replacement becomes necessary, choosing a quality battery that meets your vehicle’s specifications ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding the critical relationship between your battery health and engine operation empowers you to make informed maintenance decisions, potentially saving significant money on repairs while ensuring your vehicle remains reliable regardless of conditions or seasons. By responding promptly to the symptoms of a failing car battery, you’re not just addressing one component—you’re protecting your entire vehicle’s electrical and mechanical systems.